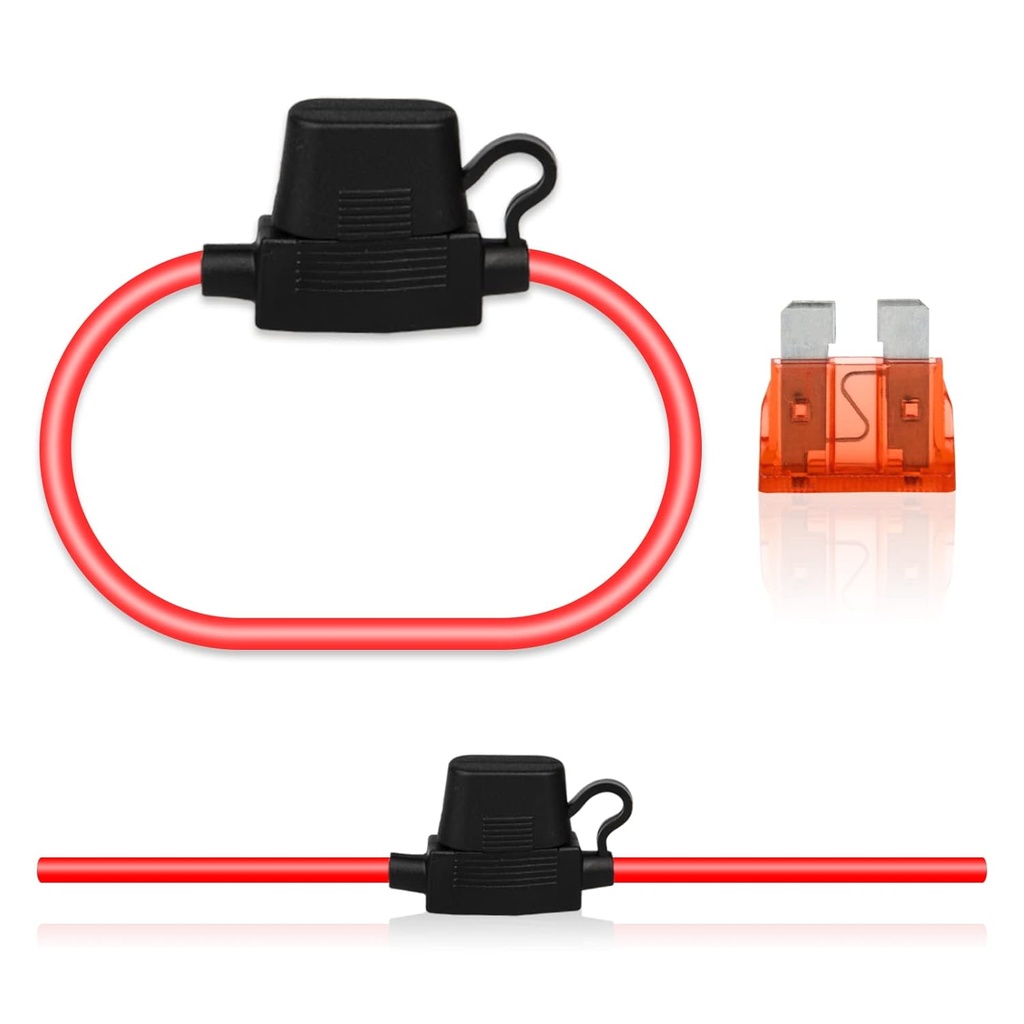
PLUG IN FUSE HOLDER
A plug-in fuse holder is a device used in various electrical applications to protect circuits from damage caused by overcurrent conditions. Unlike the inline fuse holder which is spliced into a wire, a plug-in fuse holder offers a more convenient and modular approach. Here's a breakdown of its key characteristics: Types: There are two main types of plug-in fuse holders: Panel-mounted: These holders are designed to be installed within an electrical panel or enclosure. They typically have a base that mounts on a panel surface and a socket that accepts a plug-in fuse carrier. Chassis-mounted: These holders are designed to be mounted on a flat surface, such as a chassis or wall. They often have a similar design to panel-mounted holders but may have additional features like a switch for disconnecting the circuit. Components: Fuse Carrier: This is a removable plug-in component that holds the fuse. It has a base that plugs into the socket of the holder and a housing for the fuse itself. Socket: This is the stationary part of the holder that accepts the fuse carrier. It provides electrical connection and ensures proper placement of the fuse. Applications: Plug-in fuse holders are used in various electrical systems for convenient circuit protection, including: Automotive: Protecting accessory circuits in vehicles, allowing easy fuse replacement without accessing the main fuse box. (Less common than inline holders in automotive applications) Appliances: Protecting circuits in some appliances, particularly for modular components or replaceable power cords. Industrial Equipment: Protecting individual circuits within control panels or machinery. Audio/Video Systems: Protecting speaker circuits or other components within entertainment systems. DIY Electronics Projects: Providing a safe and accessible way to incorporate fuse protection into custom circuits.